EMG
What is it?
An electromyogram (EMG) looks at the function of the nerve roots leaving the spine. It does this by looking at how well the electrical currents in the nerves are being transmitted to the muscles. Pressure on the nerves or damage to the nerves changes the way they transmit electrical current. This shows up in the muscles as they react to the information being sent to them from the brain by the nerves. When ordering electrical tests to diagnose spine problems, EMG is combined with a test showing electrical signals going from the body to the brain, called somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs).
Why is it done?
By looking for abnormal electrical signals in the muscles the EMG can show if a nerve is being irritated or pinched as it leaves the spine on its way down the arm or leg. The EMG is similar to testing the wiring on a lamp. If a working bulb is placed into the lamp and it lights up, you can assume that the wiring is okay. If the bulb does not light up you can assume that something is probably wrong with the wiring-the lamp is unplugged or a short circuit has occurred. Using the muscles like the light bulb in the lamp, the EMG is able to determine the condition of the nerves that supply those muscles, just like the wiring on the lamp. If the EMG finds that the muscles are not working properly, your doctor can assume that the nerves must be getting pinched somewhere.
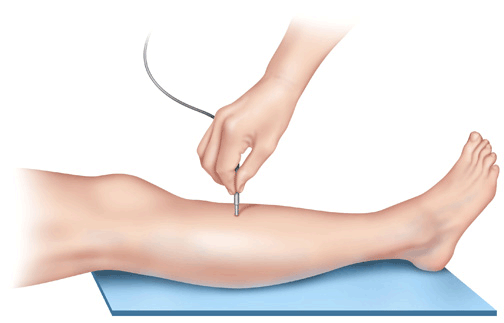
How is it done?
Tiny electrodes are inserted into the muscles of the legs. The nerve going to the muscle is stimulated to see how long it takes the electrical signal to reach the muscle and make the muscle tighten.
What are the limitations?
An EMG does not show why the problem occurred or what is causing it. The test looks primarily at how the muscles are reacting to the nerve problem. But there could be a problem in the nerve somewhere between the spine and the muscle, and it may not necessarily be in the spine itself. Still, an EMG is helpful in determining how much the nerve is being damaged and if there is a herniated disc or other source of pressure on the nerve roots. Also, the test may appear normal when the nerve is damaged. This is called a "false negative," meaning the test results look negative, even though they are actually positive.
What are the risks?
There are few risks associated with an EMG. Anytime a needle is inserted into the body there is a small chance of infection. But the risk is almost absent in this type of test.
